Business goals are key for establishing your organization’s priorities, aligning your teams’ and employees’ activities towards common objectives, and setting your company up for success. It’s always worth it to take the time to properly set business goals, as well as break them down into separate objectives for individual teams and members. It will immensely boost your ability to accomplish your goals.
Join the KeepSolid Goals team as we investigate the definition of business goals and objectives, look at some examples of short- and long-term business goals, define SMART goals, and learn to set them!
Business Goals Definition
Business goals are the objectives that a business strives to accomplish in a set period of time. You set business goals for your whole company in general as well as for individual teams, workers, managers, etc.
A goal manifests a company's larger purpose, something global that a business and its teams work toward. Business goals and objectives do not have to have clearly defined actions or be too specific. Quite the opposite, they represent broad results that the organization yearns to achieve.
Why setting business goals is important
- Goals provide a clear way to measure progress (are we getting closer or farther from our goal?)
- Business goals keep all employees and stakeholders on the same page as to what the company is trying to achieve
- Goals communicate to employees the basis of your organization’s decisions
- They give the whole company clarity of direction (Are we getting closer to the goal? Good, then we’re moving in the right direction)
Setting Business Goals with SMART Framework

SMART is an objective-setting framework that describes the characteristics that a good business goal must possess. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable (Attainable), Relevant, Time-based (Time-bound).
Accordingly, business goals should be:
- Specific - clear enough that everyone understands the steps necessary to achieve them
- Measurable - have some innate way to evaluate whether you’re making progress toward it or not, i.e. milestones
- Achievable - one that your company can reasonably accomplish within a set timeframe
- Relevant - aligned with your organization’s values and global objectives
- Time-based - have a clear time frame and deadlines
Example of a SMART business goal
- Business goal: Increase the company’s profits.
- Specific: Increase revenue while decreasing expenditure. Cut rent by 7% by moving to a more affordable premise to reduce the operational costs.
- Measurable: Grow sales over the next three months by attracting 30 more potential clients.
- Attainable: Improve customer relationships and promote the business through networking, social networks, and referrals, which will bring more leads and therefore will increase the business’ revenue.
- Relevant: Relocating to a cheaper place will allow us to grow profits by reducing the operational costs.
- Time-bound: Increase the company’s profit by the end of the coming three months.
How to Set Business Goals
Objectives that your organization is planning to achieve in weeks or months are considered short-term business goals. If longer, they’re called long-term goals. Setting business goals takes 5 steps:
1. Identify your organization's priorities
First of all, to set business goals one needs to understand what their business aims to achieve in a set period. Often, short-term business goals stem from the long-term ones and facilitate them. So when choosing both short-term and long-term goals, consider how they will propel your business forward.
2. Break down each goal into Key Results
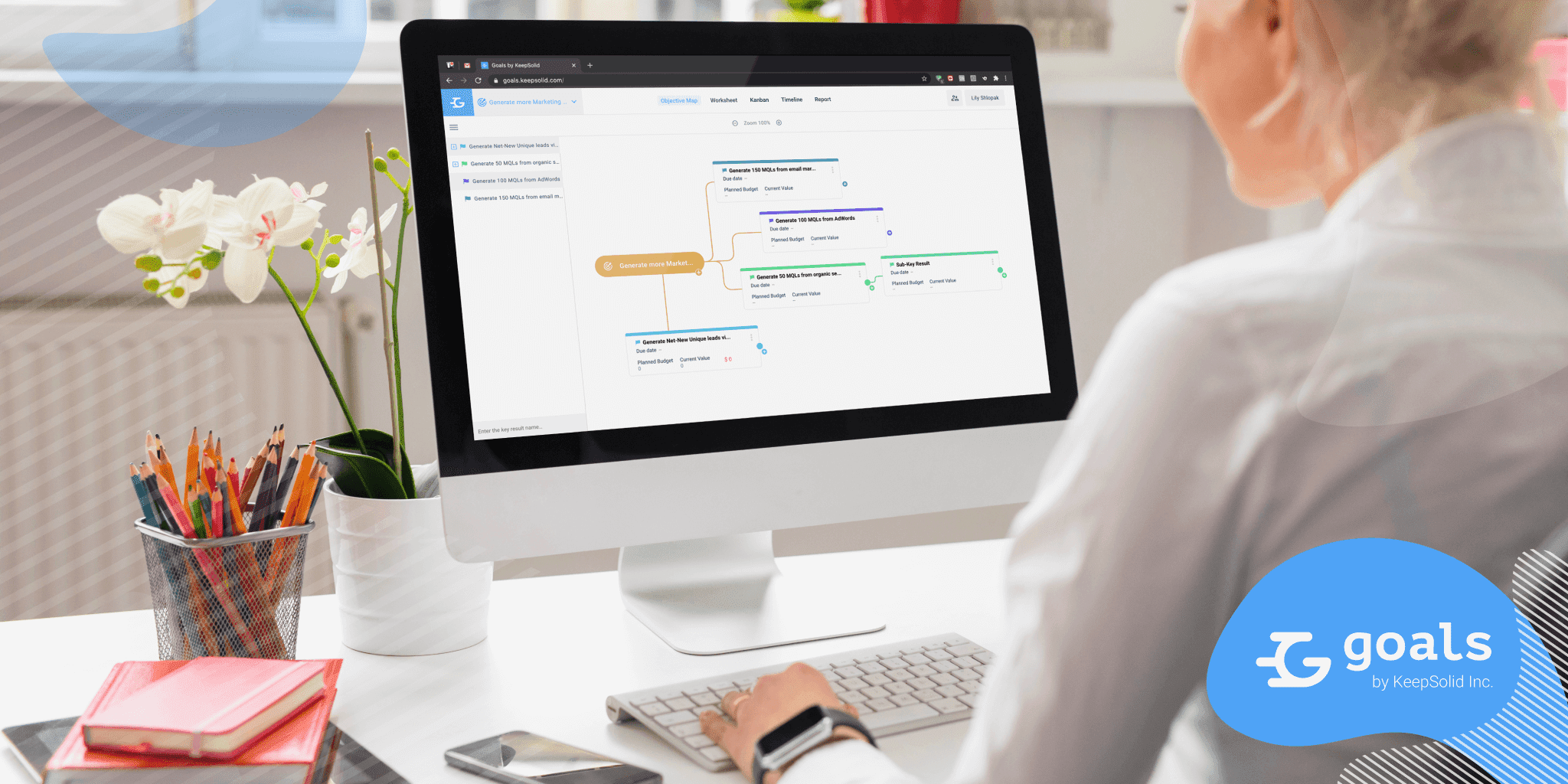
Next, break down each business goal into sub-goals, also known as Key Results. They are a part of the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) framework, where Key Results represent the milestones that your business should achieve on the way to the goal. For example, if your short-term goal is to optimize customer acquisition, your Key Results would be “improve the marketing automation process” or “reduce the Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)”. At the same time, for long-term goals, Key Results often equal to respective short-term goals.
3. Keep your Key Results concrete and measurable
As opposed to business goals that are expected to be more broad and general, Key Results should always be measurable. For example, if you need to post more on social media to reach a business goal, simply stating "post more on social media" is not a Key Result. Instead, make it measurable and specific, e.g. "post on Facebook two times a week and Instagram three times a week for two months."
4. Assign goal-related tasks to employees
At this step, assign relevant tasks to each Key Result. These tasks are the steps that should be taken to achieve their respective Key Results. Each task should be assigned to specific teams or employees who will see the task through to completion.
5. Manage your strategy and track progress
Setting business Objectives and Key Results, assigning and managing tasks, monitoring the team, and tracking progress towards set goals is a complex undertaking. It’s always recommended to use dedicated tools for this, such as KeepSolid Goals. This app provides you with plenty of tools for managing business goals and tracking progress.
We could go on describing all its benefits for setting business goals in great detail. But, as always, your personal experience is worth a thousand words, so why not try KeepSolid Goals for FREE yourself?